Borie Fasteners is a professional Pull Thru rivet manufacturer and supplier, we are committed to providing you with superior fastening solutions. Pull Thru rivet customized available in material, length, diameter, surface treatment.
Standard:
Pull-thru pt rivetDiameter:
3.2mm/4.0mm/4.8mmHead Type:
Dome Head/Countersunk Head/Large FlangeMaterial:
Aluminum/Steel/Stainless Steel/Copper/Brass/MonelCertificate:
ISO9001/IATF16949Finish:
zinc plated/paintedFactory:
We are a factory with 19 years of R&D experienceMOQ:
50000pcsDouble Countersunk Pull Thru Through PT Rivets
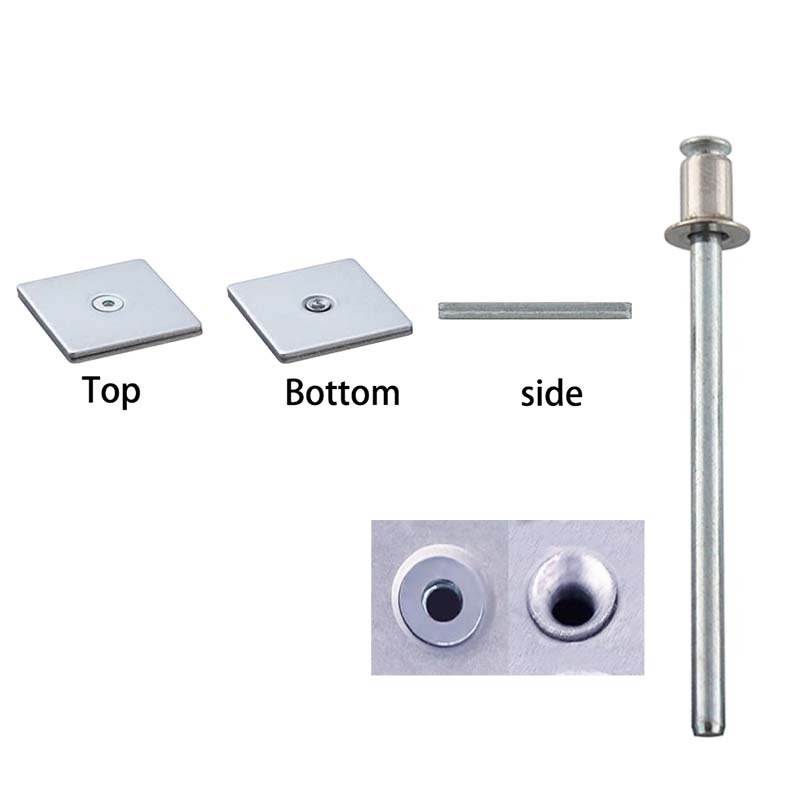
A Pull Thru rivet, also known as a PT rivet or double countersunk rivet, is a type of fastener used to join two or more materials together. It consists of a cylindrical body with a mandrel, or pull stem, passing through the center. The rivet is inserted into a pre-drilled hole and then pulled into place using a specialized tool, such as a rivet gun.
As the mandrel is pulled, it deforms the rivet body, creating a tight joint. The excess mandrel is then snapped off, leaving a neat and flush finish. Pull Thru rivets are ideal for applications where access is limited to only one side of the workpiece, hence their name "blind" rivets.

Material (Body/Mandrel)
Steel/ Steel
Stainless steel/ Steel
Color painting is available.
Diameter sizes: 3.0mm
Advantages
1. High load-bearing capacity.
2. Easy installation.
3. Provides a secure and tight joint.
4. No need for access from both sides.
5. Suitable for use in thin or brittle materials.
6. Resistant to vibration and fatigue.
7. Offers excellent retention and sealing capabilities.
NOTE: PT rivet is designed for the products that require a flush set after riveting, so both sides of the workpiece must be countersunk holes.
How Does Pull Thru rivet Work?
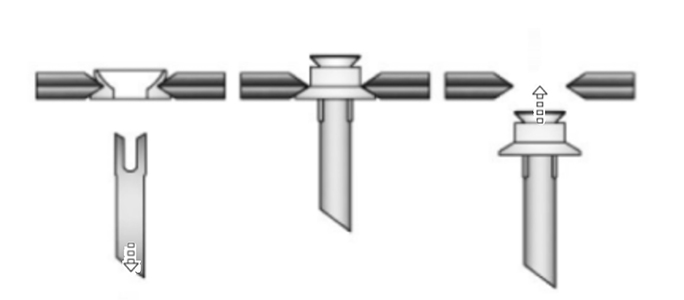
1. Gather the necessary tools and materials: Pull Thru rivets, a rivet gun, and a drill with an appropriate-sized drill bit.
2. Mark the locations where the Pull Thru rivets will be inserted, ensuring they are appropriately spaced and aligned.
3. Use the drill to create holes at the marked, making sure the hole size matches the diameter of the rivets.
4. Insert the Pull Thru rivet into the drilled hole, with the mandrel or stem protruding from one side.
5. Place the rivet gun over the mandrel or stem of the rivet.
6. Squeeze the rivet gun's handles together to secure the rivet in place.
7. Continue squeezing the handles until the mandrel or stem breaks off at the predetermined load, leaving the rivet firmly in place.
8. Repeat the process for the remaining Pull Thru rivets, following the marked locations.
9. Inspect the installed rivets to ensure they are secure and properly aligned.
10. Clean up any debris or excess material resulting from the installation process.
Note: It's essential to refer to the specific manufacturer's instructions and guidelines for the Pull Thru rivets being used, as the installation process may vary slightly depending on the product and application.
ST/ST Pull Thru Rivets
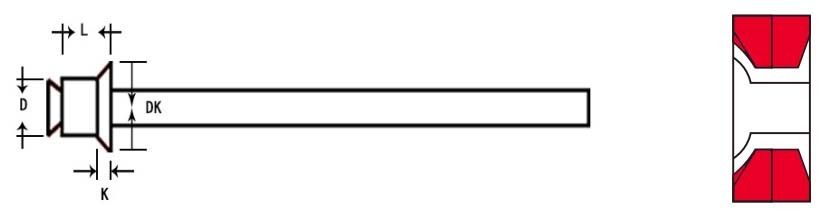
| RIVET DIAMETER /mm |
RIVET LENGTH /mm |
GRIP RANGE /mm |
HEAD DIAMETER /mm |
HEAD HEIGHT /mm |
MANDREL DIAMETER /mm |
MANDREL LENGTH /mm |
HOLE SIZE /mm |
SHEAR /N |
TENSILE /N |
| D1 | L | 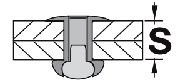 |
DK | k | d | p | DRILL |  |
 |
| +0.1/-0.2 | MAX. | -0.2/+0.4 | ±0.2 | REF. | MIN. | MIN. | MIN. | ||
| 3.0 +0.05 -0.15 |
2.1 | 1.60 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 2.00 | 26.00 | 3.1-3.2 | 1100 N | 900 N |
| 2.4 | 1.6-2.0 | ||||||||
| 2.6 | 1.8-2.3 | ||||||||
| 2.8 | 2.0-2.5 | ||||||||
| 3.0 | 2.3-2.8 | ||||||||
| 3.3 | 2.5-3.0 | ||||||||
| 3.8 | 3.0-3.5 | ||||||||
| 4.3 | 3.5-4.0 | ||||||||
| 4.8 | 4.0-4.5 | ||||||||
| 5.3 | 4.5-5.0 | ||||||||
| 5.8 | 5.0-5.5 | ||||||||
| 6.3 | 5.0-6.0 |
Production Process
Step 1
Blind rivet machine---making the rivet body
Step 2
Nail making machine---making the mandrel
Step 3
Assembly machine--finish the assembly of rivet body and the mandrel

Package
Regular package is small box+ carton+ pallet, or bulk in carton, each carton weights 20-25kgs.
Borie Fasteners can also provide custom packaging service, such as poly bag or plastic bag with client's logo and information.

Application
PT Blind rivets can be used just about anywhere if they are properly installed. Most of them are used in
1. Automotive manufacturing
2. Aerospace industry
3. Electrical enclosure assembly
4. Furniture manufacturing
5. Marine industry
6. HVAC systems
7. Metal fabrication
8. Railway industry
9. Construction industry
10. Consumer electronics manufacturing
